Solar Collectors
The primary purpose of solar hot air collectors is to heat air that is used in ventilation or air-tempering systems. By design, these are very simple devices, usually consisting only of a light frame, an absorber, glazing and sometimes a ventilator for propelling the air through the collector. Since no fluid is flowing through them, they do not need to be water-proof and they can neither leak, nor freeze.
The disadvantages of this system is a worse heat transfer between the absorber and the air as well as the lower specific heat of air when compared to collectors with water-based heat transfer fluids. In order to extract a required amount of energy, the area of the absorber needs to be widened and airflow increased. For heat accumulation, hot air is often led into accumulators containing solid materials, such as rocks.
Here are three types of air based solar collector designs:
An unusual implementation of solar collectors into the whole architecture of the estate.
Unglazed collectors
The absorber with selective coating is exposed directly to the sunlight. Higher convection heat losses are compensated by zero glass reflection. Since the design is so simple, it is widely used to pre-heat ventilation air for which purpose a black perforated absorber is frequently installed on the facade of a building.
Glazed collectors
The absorber is covered by a translucent cover which increases the efficiency of the collector by reducing its heat losses. These collectors can reach higher temperatures and they can be connected to air conditioning or heating systems. An interesting feature may be the incorporation of a ventilator powered by a photovoltaic solar panel. If the sun is shining, the hot air is automatically propelled by the ventilator to the point of consumption.
Closed system hot air collectors with a heat accumulator
Glazed collectors accumulate heat in solid material accumulators (such as rocks). Functionally, they are similar to fluid based thermal collectors. The only difference is that here the heat transfer medium is air.
“Sunshine duration” is a period of day during which the value of direct irradiation by the Sun does not drop under 120 W/m 2.
Flat-Plate Collectors
Video: Flat-plate collector.
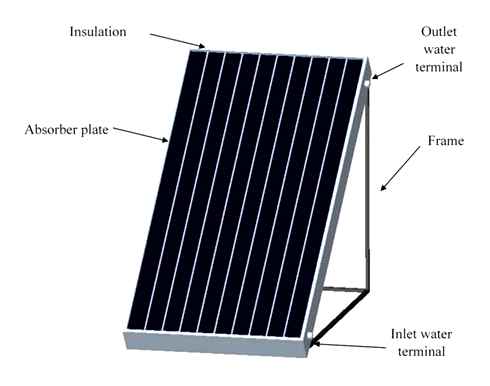
Flat plate solar collectors are basic building blocks of water-heating solar systems and in some cases as a secondary heat source in heating systems.
A flat plate collector power output depends on many factors. The main factor is the amount of solar energy falling on the surface of the collector. To achieve maximum gain, a collector should be irradiated all day long, facing the right direction and the surface should be perpendicular to falling sun rays. A southerly to south-westerly orientation is ideal. The inclination should be set with respect to the Sun’s path in different seasons, or it should be variable. In central Europe, the best yield is reached at 20 to 30 degree inclinations in summer and at 60 degrees in winter. In practice, variable inclination is not used very often. Collectors are inclined to maximize output at transitional periods that means approximately 50 degrees in central Europe.
The working principle of a solar collector is to capture solar radiation in a copper or aluminium collector which heats up and gives its heat to a heat transfer medium that circulates in pipes. The absorber is coated in a black selective paint which increases heat absorption of diffuse radiation thus making the collector more efficient. To minimize heat loss, the absorber is insulated from the frame, using conventional insulating materials, and is covered by a glass plate or a translucent plastic cover.
Flat plate solar collectors can be 70 to 80% efficient and have a life span of approximately 30 years. They can save up to two thirds in heating energy expenses.
Installing a collector inclination control mechanism can increase perennial yield by 40%.
The optical efficiency of solar collectors is the ratio between the amount of radiation falling on a reference area and the amount of radiation transformed into heat. Its value is usually close to 0.9.
Evacuated Tube Collectors
Video: 3D model of an evacuated tube collector. Vacuum Collectors — reach, due to good insulation properties, better utilization of solar radiation than other types of thermal solar collectors.
Evacuated tube solar collectors use a vacuum for insulation. Thanks to this design they lose less heat than other types of collectors and they reach higher efficiency at less irradiated sites and lower outside air temperatures.
From a design point of view, collectors can be categorized by the number of walls of vacuum tubes, into single-walled and double-walled, or by the means of heat transfer, into heat pipes and U-pipe collectors. The U-pipe concept, where the heat transfer medium flows directly through the absorber in loops, is a less complex solution. The heat pipe, on the other hand, is in fact a binary cycle system. The tube is filled with a low boiling point substance. This substance evaporates as it is heated and ascends to the condensation zone where it loses its heat to a heat transfer medium. Then it condenses and returns in liquid state back to the bottom part of the tube.
A detailed view of an evacuated tube collector coated with a dark-absorbing paint.
Single-walled evacuated tube solar collectors consist of a glass-evacuated tube with a flat, selective surface absorber on the inside. The absorber is attached to the heat pipe or U-pipe. The metal pipe from the absorber has to go through the glass wall of the tube without compromising the insulating vacuum which represents a certain weak point in the design. The transition must be very tight.
A double walled evacuated solar collector consists of two glass tubes, one inside the other, working on the same principle as a vacuum flask (a thermos). The air from the space between the two tubes is evacuated to reduce heat loss of the absorber to its surroundings. The outer surface of the inner tube is coated with a special selective paint with excellent radiation-absorbing properties. The absorber itself is inside the inner tube in a non-evacuated environment. To allow for a smooth transfer of heat from the absorber to the heat transfer medium, a special segment, which ensures good contact, is used to connect the tubes. The lower part of the evacuated tube is coated with barium from the inside. The coating absorbs any atmospheric residue and it turns from silver to white once vacuum integrity has been compromised.
Open solar collectors
This is the most primitive and simple type of solar collectors. It is a plastic container with water and a surface made of plastic or rubber, which absorb the sun’s rays well. Usually, open collectors are used only in summer in private houses, in summer cottages for heating water in a pool or outdoor shower. The surface of such a collector is not covered with glass. With a low cost and simplicity of design, this type of collector has a low efficiency, as well as a short service life (from 1 to 3 years). Since the performance of this type of collector directly depends on weather conditions and ambient temperature, it is advisable to use it only in the southern regions of the country.
Air solar collectors
These solar devices are used for heating and air conditioning in rooms, drying plants, air recovery systems, etc. Such collectors are less common than vacuum or flat ones, and the role of the heat carrier in them is played not by liquid, but by air.
The design of the air collector is a ribbed (sometimes perforated) metal plate with a selective black coating or a system of metal tubes with good thermal conductivity. The air collector works on the principle of forced or natural supply of air heated by the action of sunlight into the room. The device is connected to the room by means of air ducts for air supply and intake, in which fans are installed that provide convection and circulation of air masses. The air itself is heated by direct contact with the heat-conducting metal, which has absorbed the energy of the sun’s rays. The design of the air collector is reliable and simple, the service life reaches 10 – 20 years. Of the minuses – the use of additional energy for fans, which increases the cost of its operation.
Flat solar collectors
The flat plate solar collector has a layered structure. In fact, this is a plate of heat-intensive metal, which can be coated with a black selective composition that promotes better absorption and transformation of sunlight with almost zero reflection – the so-called absorber. From below, thin tubes are welded to the plate – parallel or winding (in the form of a coil tube) – a heat-transfer fluid circulates through them. The sun’s rays absorbed by the absorber warm up the coolant, and then the heat is transferred to the system.
The absorber (plate) is placed in a heat-insulating housing made of aluminum profiles, and on top it is covered with protective (ordinary or tempered) glass with minimal light transmission to create a kind of “greenhouse effect”. To minimize heat loss, it is important to make reliable thermal insulation between the walls of the housing and the absorber. As a rule, the heat-insulating layer is laid in a continuous plate under the absorber plate.
Externally, a flat solar collector looks like a solid and bulky slab, it is not easy to install, especially on roofs with a steep slope. The disadvantages include also significant heat losses in the cold season, even with a sealed case and a good heat-insulating layer. Due to the design features, the efficiency of such a solar collector may be low even with a good level of absorption of sunlight. Therefore, it makes sense to use flat-plate collectors mainly in the summer season.
Flat- plate vacuum collectors. a type of flat-plate collectors, are more efficient. In this type of device, losses are minimized by the vacuum between the absorber and the glass. At the same time, the efficiency of the collector increases, since the interaction of the absorber plate and glass is minimized, and the system itself works on the principle of mirror reflection, regardless of the angle of incidence of the sun’s rays. With a higher efficiency, which is a plus, the disadvantages include the complexity of installation and the high cost of a collector of this design.
Tubular vacuum solar collectors
This type of solar collectors is the easiest to install and at the same time has the best efficiency in comparison with flat collectors. In all devices of this type, regardless of the manufacturer or type of construction, there is a vacuum, and the principle of mirror reflection also works, which increases the efficiency of work.
The main and fundamental difference between tubular collectors and flat collectors is the shape of the absorber. To convert solar energy into thermal energy, instead of a plate, an evacuated tube (pipe system) made of special glass with a metal rod inside it with a heat transfer fluid and a selective coating is used here. Tubular vacuum solar collectors are equipped with a special frame and can be mounted in parts – this explains their ease of installation.
The design of such a collector is a hydraulic network, where the tubes are attached to the heat exchanger body and communicate with it through thermal channels located in the middle of the absorbing plate. However, the body-heat exchanger itself and the tubes can have a different design and principle of operation.
The classic direct heating coaxial tube is quite simple and similar to a thermos. It is a flask with two walls, between which there is a vacuum. A rod (most often copper) is used as a thermal channel inside such a tube. With this design, the heat channel is in direct contact with the heat-absorbing surface of the absorber, so heat losses in collectors with such tubes are very small. These collectors work mainly seasonally, in summer, and at a pressure not higher than 0.2 atm. They are low cost and easy to install.
Coaxial vacuum tube with U-type system
The heat exchanger inside each tube of this type has a U-shape, is located inside the tube and is integral with it. Such devices are considered highly efficient, give minimal heat loss, and are easy to install. The downside is the high price, labor intensity and high cost of repairs – if one of the structural elements fails, all the others must be replaced.
Coaxial vacuum tube with thermotubes or with heat-pipe system
Inside the copper tubes of this type of collector there is a rapidly boiling liquid (a mixture of water, nitrogen-like mixtures, ammonia, aldehyde, methanol, etc.).
The rays of the Sun, falling on the wall of a thermotube of this type, heat it up, the liquid boils, evaporates and transfers the heat received in the form of rising steam to the heat exchanger. Then, having given off heat, the liquid in the form of condensate returns to the thermotube. Such thermotubes are connected to the heat exchanger using special devices (sleeves) and together form a heat-pipe system (hot pipe).
Solar collectors with such a tube arrangement are easy to install and repair, have a low cost and can work productively in any weather. Practice shows how such solar collectors work in winter – they are effective up to severe frosts (down to.30-35Cº).
Feather tubes with heat-pipe system
These tubes are considered the most efficient, productive and modern. They have a slightly different structure, but the principle of operation is the same as in coaxial tubes.
Feather tubes are flasks with one strong and thick wall, inside of which there is a copper heat-absorbing tube with a corrugated plate and an absorption layer. Thanks to this design, the vacuum is formed directly in the heat channel, and the heat channel and absorber are partially integrated into the flask. The heat-pipe system with a feather absorbent plate and a thermal channel embedded in it is half-open and immersed in vacuum with the open side.
Solar collectors with this type of tubes are characterized by high efficiency. At the same time, they are quite expensive in cost, complex and costly to repair – if one element fails, the entire system has to be changed.
There is also such a type of solar collector as a vacuum collector with direct heating coaxial tubes (with direct heat transfer) and with a tank with a heat exchanger built into it. Here, the heat exchanger, which is supplied with steam from a boiling liquid, is built into a metal tank. After heat transfer, the liquid returns to the tube in the form of condensate. In such a device, heat loss is minimal, the system is highly efficient and can operate even at very low ambient temperatures (down to.30-35Cº).
In solar collectors, the types of tubes and thermal channels can be combined with each other in different ways. And each combination will have its own performance characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, in order to best choose the design that suits you and find out how much solar collectors cost, you need to correctly formulate the task assigned to it and, for reliability, turn to professionals to select and calculate the system.
Types of solar collectors
The TS300 vertical solar collector with 50mm thermal insulation is one of the most common solar collectors in Europe. This solar collector is suitable for small and large solar collector systems for water heating, heating support and swimming pool heating. These collectors are mounted in parallel.
Maximum number of collectors in one row. 10.
Horizontal solar collector TS330 with 50mm thermal insulation
TS330 Thermo|Solar solar collector is specially designed for horizontal mounting. These solar collectors are used mainly when required by the architecture of the building. They are often used as balcony railings, small awnings, etc. It is also recommended to mount them on the roofs of high buildings, where there is a high wind load and it is not possible to securely fasten vertical solar collectors. These solar collectors are mounted in parallel.
Maximum number of collectors in one row. 5.
What Are the Different Types of Solar Collectors?
There are many solar thermal collector types. The solar collector used will depend on the use that is going to be given to it. The classification of solar thermal collectors in the solar energy market is the following:
Flat Plate Collectors
Flat solar collectors capture the solar radiation received on a surface to heat a fluid. The greenhouse effect is often used to reduce heat loss.
The core of this type of flat plate solar collector is a set of vertically oriented metal tubes that conduct cold water in parallel. These pipes are connected at the bottom by a horizontal pipe to the cold water intake and another similar pipe to the outlet at the top.
The tubes are encased by a cover at the top, which is usually double glass, and at the bottom by an insulating material.
This type of solar collectors are used in low-temperature installations (below 80 degrees Celsius), such as for heating swimming pools.
Evacuated Tube Collectors
An evacuated tube solar collector is similar to a flat plate solar collector, but glass tubes replace the metal tubes. These glass tubes are encapsulated, one by one, in another glass tube between which a vacuum is made for insulation.
This type of thermal solar panel has a higher performance, but its cost is higher.
Concentrating Collectors
This type of collector captures the radiation received on a relatively large surface and concentrates it using flat mirrors or parabolic troughs on a smaller surface.
The objective of FOCUS collectors is to concentrate the solar energy received on a surface at one point to obtain high temperatures. This technique is used in high and very high-temperature solar installations.
Usually, this type of solar collector is used to generate the very high-pressure water vapor and electricity as in a conventional thermal power plant.
Components of a Flat Plate Solar Collector
The cover: The cover of a solar collector is transparent. It may or may not be present. It is usually made of glass, although plastic is also used. Its function is to minimize heat losses by convection and thermal radiation.
Air channel: It is a space that can be empty that separates the cover from the absorbent plate. Its thickness is calculated by considering the purpose of balancing convection losses and the high temperatures that can occur if it is too narrow.
Absorbent plate: it is the element that absorbs solar energy and transmits it to the liquid that circulates through the pipes. The main characteristic of the plate is that it must have high solar absorption and low thermal emission.
Most Useless Degree? #shorts
Tubes or ducts: these elements touch (sometimes welded) the absorber plate so that the energy exchange is as large as possible. The liquid circulating throw the pipes that will be heated and go to the accumulation tank.
Insulating layer: The purpose of the insulating layer is to cover the system to avoid and minimize losses.
Use of Solar Collectors
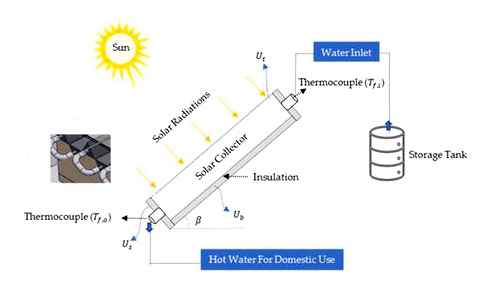
Solar collectors mainly supply hot water for DHW and heating or generate electricity.
In the case of collectors for domestic hot water and heating, the Solar storage tanks the domestic water that contacts the fluid using a coil. The coil allows the fluid to transfer the stored heat energy to the water without contaminating the water.
This water can be used as hot water in homes (80% integration) or to complement the floor heating of the rooms (10% integration). Thermal solar collectors can supply hot water in abundance but cannot completely replace the usual heating methods due to the lack of solar energy.
Solar collectors intended for electricity generation require that the heat exchanger be heated until it is boiling. Once the liquid has completed the thermodynamic phase change and has passed into the gas phase, it is sent to a thermoelectric turbine that will convert the movement of steam into electrical energy.
This type of system is called solar thermodynamics and requires large spaces for installing solar panels and a constant presence of the sun. Examples of these plants have been installed in the deserts.
Published: September 28, 2015 Last review: June 21, 2022
