Top Solar inverter manufacturers in Germany
Two years later – following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant disaster in 2011– it announced major policy decision that lived up to this tag, announcing that it would do away with nuclear energy totally by the year 2022.
Today, it is estimated that a little over 30% of its total power requirement is met by green energy sources; the target is to reach 50% by 2030.
The development has spelt companies manufacturing renewable energy products such as solar inverters; according to industry estimates, there are over 1.4 million solar PV systems in Germany.
While some of these companies are the solar divisions of multi-sector multinationals, there are also standalone companies dedicated to solar energy products.
Short list of such companies making solar inverters in Germany is given below:
According to the data gathered by Canadian market research company Technavio, the global solar PV inverter market is rising at a CAGR of nearly 15% as far as revenues are concerned.
SMA Solar Technology AG
Headquartered in Niestetal near the city of Kassel in northern Germany, the SMA Group is easily the biggest player in the German solar inverters, a key unit of all PV plants.
over, its total turnover of about €1 billion in 2015 also makes it the market leader globally. The group has operations in 20 countries, employing more than 3,000 people worldwide.
According to the “PV Inverter Customer Insight Survey 2016” by IHS Markit, which tracks corporate performance and national economies worldwide, SMA Solar Technology AG (SMA) was voted the most preferred inverter brand in the world by all customer groups. This was for the fifth time that the company was thus rated.
The IHS Markit survey covered wholesalers, installers and EPC companies in more than 45 countries, who rated SMA the best for its quality, technical support and service.
Kaco New Energy GmbH
Following SMA in the pecking order is Kaco New Energy, also one of world’s largest manufacturers of solar inverters globally.
Headquartered in Neckarsulm near Stuttgart, Kaco has businesses in 16 countries, with its production facilities in Germany, the Americas and Asia having produced inverters with a total capacity of around eight GW since 1999.
In 2014, Kaco observed the centenary of the original company, one of the first suppliers of inverters in the late 1930s.
Kaco’s inverters, which come in a wide range of sizes, cater to an entire spectrum of customers – from the small residential units to large solar farms of hundreds of Megawatts.
Kaco New Energy’s product range spans battery inverters, energy storage systems, inverters for PV-diesel hybrid systems as well as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems.
In2016, it introduced new three-phase inverters – the Blueplanet 8.6 TL3 and the 10.0 TL3, which are suitable for residential and commercial-scale PV systems, and the Blueplanet 20.0 TL3 that meets the needs of commercial systems as well as industrial-sized power plants.
ABB
A Zurich, Switzerland-based MNC, ABB has operations across the world including Germany and India, its German operations being headquartered in Mannheim.
It also boasts of one of the broadest solar inverter portfolios in the industry, the product range covering small micro-inverters, the three-phase string inverters and megawatt-sized central inverters.
Its broad array of solar inverters fit in with the power plants that are called multi-megawatt PV as well as the smallest residential photovoltaic systems, commonly known as PV.
ABB has over 40 years of experience in the solar inverters sector.
Fronius International
Established by Günter Fronius in Pettenbach, Austria in 1945 and named after him, Fronius began by manufacturing battery chargers and welding transformers.
Today, it is known for its highly functional grid-connected inverters that work with all standard solar modules, and till about 2009, was the third biggest player in the inverter sector in neighbouring Germany.
Fronius began kits Energy Environment Division in 1995, with business units for battery charging systems and photo-voltaics. The same year, it launched the “Sunrise” which is a grid-connected solar inverter. It not only generates electricity from solar energy but feeds it into the power grid as well.
Two years later, the Sunrise solar inverter won the “Innovation Prize” offered by the Province of Upper Austria.
General Electric
GE’s German operations, located out of Berlin, delivers innovative solutions for utility scale PV power plants based on its solar inverter, the core component in a solar farm, to convert solar energy into electricity to the grid.
It is part of the 140-billion transnational that also has a footprint in the solar power sector, and delivers solutions for utility-scale PV power plants based on its inverters with outputs or 700Kw and 1Mw.
Sputnik Engineering GmbH
Sputnik Engineering GmbH is the German subsidiary of Sputnik Engineering AG of Switzerland. The German operations began in 2001 in Neuhausen as a reaction to the considerable growth in demand for PV inverters.
AEI Power GmbH
Located in Metzingen in Germany’s in Baden-Wurttemberg state, AEI Power GmbH is the German subsidiary of Advanced Energy Power Solutions of the US.
With a technological revolution sweeping the world in every sector, the renewable energy segmen is no different; keeping step with it, Advanced Energy is moving ahead too, with its power conversion solutions.
Founded in 1981, Advanced Energy has been in the business for 36 years of experience, delivering advanced power and control technologies to customers from a broad swathe of industries.
The AEI has its operations spread across North America, Europe including Germany, and Asia including India.
Siemens AG
Whatever challenges posed by the growing market, Siemens has been able to develop wide-ranging answers as it is backed by decades of experience as a supplier of large-scale power plants and its standing as a trustworthy partner in the energy sector.
Today, Siemens is a one-stop supplier for all key components of solar power plants, including solar inverters.
Schneider Electric Solar
Part of the over 180-year-old French multinational Schneider group, Schneider Electric Solar is about 15 years old; it entered the solar inverter sector after acquiring Canadian inverter manufacturer Xantrex in 2008.
In Germany, Schneider is headquartered in Ratingen in North Rhine-Westphalia state.
Delta Germany
The German subsidiary of the 7.5-billion Delta Group of China, which is into power products, it makes PV inverters as well as a complete range of wind turbine converters. The company says its PV inverters deliver “industry leading efficiency” of up to 98.8%.
Guide to Solar Panel Inverters: Why They Matter (2023)
Each product and or company featured here has been independently selected by the writer. You can learn more about our review methodology here. If you make a purchase using the links included, we may earn commission.
Written by Aniket Bhor
Aniket Bhor is a solar engineer who has spent nearly a decade studying and working in the solar power sector in the European, Asian and North American markets. He recieved his Master’s degree in Renewable Energies from Germany at Technische Fachhochschule Wildau. He has since worked in the industry in a variety of capacities including Solar Energy Consultant, Business Development Head, Solar Entrepreneurship Trainer, and more recently writing for solar organizations including Venuiti Solutions, Green Integrations, Solengy, Ecotality.com. Overall, he is a climate enthusiast and avid cyclist, and he also loves to lose himself in books and cooking. Learn About This Person
Reviewed by Melissa Smith
Melissa is an avid writer, scuba diver, backpacker and all-around outdoor enthusiast. She graduated from the University of Florida with degrees in journalism and sustainability studies. Before joining EcoWatch, Melissa worked as the managing editor of Scuba Diving magazine and the communications manager of The Ocean Agency, a nonprofit that’s featured in the Emmy award-winning documentary Chasing Coral. Learn About This Person
Why You Can Trust EcoWatch
We work with a panel of solar experts to create unbiased reviews that empower you to make the right choice for your home. No other solar site has covered renewables as long as EcoWatch, which means we have more data and insider information than other sites.
Jump to Section:
Find the best price from solar installers in your area.
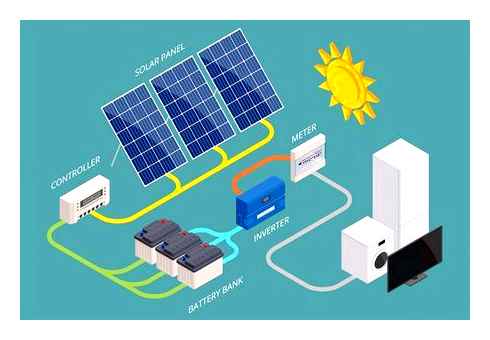
What Are Solar Inverters?
When the first power transmission lines were installed, they used what is called direct current (DC). As the name suggests, with direct current electrons travel continuously forward through a conductor. In the late-19th century, the inventor Nikola Tesla created alternating current (AC). With AC current, the electrons move back and forth through a conductor instead of traveling only forward.
With the advent of AC electricity, long-distance power transmission was suddenly transformed. Alternating current was safer and more efficient, allowing us to transmit it at high voltages. As a result, all the power grids in the coming years were designed to carry AC current. Similarly, all appliances were designed to have AC input.
Fast forward to the invention and use of solar panels. Solar panels are essentially DC devices, meaning the power flowing out of any panel is always DC. This means we won’t be able to connect a panel to an electrical appliance which is designed to have AC input. Since nearly all appliances today work on alternating current, a device that converts DC solar energy to usable AC energy is needed.
Enter solar inverters. Inverters collect DC electricity from a solar array or a battery and convert it into usable AC output. They come in various shapes and sizes and are usually rated for the system size they’re used with.
SunPower
SunPower designs and installs industry-leading residential solar and storage solutions across all 50 states. With a storied history of innovation dating back to 1985, no other company on this list can match SunPower’s experience and expertise.
SunPower earns its position as the top national installer on our list for a handful of reasons: It installs the most efficient solar technology on the residential market, offers the most expansive service area and backs its installations with a warranty well above the industry standard. All the while, SunPower pioneers sustainability efforts within the industry.
If that weren’t enough, SunPower systems come packaged with products all manufactured in-house by its sister company, Maxeon. This means that your panels, solar cells, inverters, battery and EV chargers are designed to work together and are all covered under the same warranty.
SunPower’s biggest downside? Its high-efficiency panels are considerably more expensive than most of its competitors’ products. However, its powerful panels are workhorses that make up for the initial cost with more backend production (think about this like spending more money for a car that gets more miles per gallon).
Facts and Figures: SunPower
| 5 |
| A |
| 1985 |
| Solar Panels, Solar Batteries, EV Chargers, System Monitoring |
| SunPower Panels |
| 25-year all-inclusive warranty |
Blue Raven Solar
We like Blue Raven Solar because it understands that, for most homeowners, the cost of solar presents the biggest barrier to entry.
For that reason, Blue Raven Solar developed an innovative solar financing plan that offers in-house, flexible, zero-money-down options. The results speak for themselves, as Blue Raven Solar is now one of the fastest-growing solar companies in the nation and was recently acquired by SunPower. Its BluePower Plus plan (exclusive to Blue Raven) mimics the flexible structure of a lease while still providing the greatest benefits of owning your system.
Eligible homeowners enjoy 18 months of solar power before having to pay their first bill. When coupled with the federal solar investment tax credit (ITC), the initial energy savings can offset more than a third of the overall cost of a system before requiring a dollar down.
In contrast, other installers can only offer similar financing through solar leases, PPAs or third-party providers (such as Mosaic or Sunlight). Third-party loan providers can complicate the process, while opting for a loan or PPA will disqualify you from some of solar’s biggest benefits (additional property value, federal solar tax credit and local solar incentives).
Facts and Figures: Blue Raven Solar
| 4.5 |
| A |
| 2014 |
| Solar Panels, System Monitoring |
| Trina Solar, Canadian Solar, SolarEdge, Silfab, SunPower |
| 25-year manufacturer warranty; 10-year workmanship warranty, 2-year production guarantee |
ADT Solar
ADT Solar sets the industry standard for warranty coverage by including a multifaceted guarantee, making it one of the top installers for homeowners who want added peace of mind.
Its warranty coverage includes all of the following for 25 years:
- Power Production Guarantee: Also known as a performance guarantee, this ensures your solar system will produce the amount of electricity that’s outlined in your proposal, or ADT will write you a check for the difference.
- Labor Guarantee: This covers any issues with the installation of your system and is also known as a workmanship warranty.
- Panel Module Performance Guarantee: This is what ADT Solar refers to the manufacturer warranty as, and it ensures that any manufacturing defects are repaired or your ineffective panels replaced.
- Enphase Microinverters Guarantee: This backs the performance of your inverters.
Though in recent years other solar companies have started to offer similar guarantees, ADT Solar has been at it since 2008, performing over 30,000 installations across the country.
Facts and Figures: ADT Solar
| 4 |
| A- |
| 2008 |
| Solar Panels, Solar Batteries, EV Chargers, Energy-Efficiency Upgrades |
| Silfab, Panasonic and others depending on location |
| 25-year all-inclusive warranty |
How Do Solar Inverters Work?
In the U.S, most appliances are designed to operate using AC current with an input voltage of 120 volts (V). Solar panels, as discussed above, generate DC power. Let’s take an example of a typical home solar system that generates a maximum power of 4.8 kW and has panels connected in a parallel series so that the array’s output voltage is 160 V.
In this case the inverter’s job is to bring the voltage down to 120 V while converting the current from DC to AC. It has to do this while keeping the power rating (4.8 kW in this case) constant. This is done by increasing the current rating (since power = voltage x current).
To get a bit more technical, the inside of an inverter is somewhat similar to a generator — it has a conducting coil and rotating magnets. Depending on the polarity, magnets pull or push electric current, so rotating magnets will alternately push and pull current, creating alternating current.
An extremely simple mechanism like this will give us a coarse output that looks like a square sine wave if you plot it on a graph. Modern inverters refine this power output to be smoother and more efficient. It looks like a pure sine wave when graphed — hence inverters are also called pure sine wave inverters.
Types of Solar Inverters
Since their advent, solar power systems have undergone massive changes and branched into several types including grid-tied systems and off-grid systems. These different types have evolved to incorporate specifically designed components. Inverters have also evolved to accommodate the changes and advances in solar energy systems.
Although the basic principle of all inverters is alike (power conversion between DC and AC), there are different options available on the market. Each has pros and cons. Let’s dive into the types of solar inverters and how they differ.
Microinverters
A major milestone in the history of solar power inverters was the birth of microinverters. As the name suggests, microinverters are smaller inverters that can be attached to individual solar panels instead of the entire string or array of solar panels. Some solar panel manufacturers also offer panels with microinverters integrated into the panel.
The main advantage of this arrangement is that shading or debris on one panel does not affect the entire string or array, unlike with conventional inverters. Despite the relatively lower efficiency of individual microinverters compared to string or central inverters, the combined output of a string/array with microinverters is always higher. While microinverters are becoming more common with time, a constraint on their adoption is their higher cost per watt.
If you want the benefits of a microinverter while paying less, you can opt for a cost-effective combination of string inverters and power optimizers. Power optimizers (such as those offered by SolarEdge) are DC/DC converters which convert only voltage and allow panel monitoring and optimization and can be attached to individual modules.
| Pros of Microinverters | Cons of Microinverters |
| High electricity yield | expensive up-front |
| Long lifespan | |
| Allows monitoring for individual panels |
String Solar Inverters
Solar panel systems are installed in three stages: installing individual solar panels, then wiring them into strings, and finally joining all the strings to create an array. Inverters can be attached to the solar panels at any of the three stages. As we’ve discussed, inverters attached to single panels are microinverters and those connected to strings are string inverters.

String inverters are some of the oldest and simplest types of inverters. They are also cheaper in comparison to microinverters, but suffer from significant voltage drop even if only one panel’s power output is reduced due to shading or snow.
| Pros of String Inverters | Cons of String Inverters |
| Relatively inexpensive | Lower electricity yield |
| Easy to maintain | Shorter lifespan |
| Lower cost |
Hybrid Inverters
For many years, the biggest, and probably only, disadvantage of grid-tied systems was that they stopped functioning in the event of a power outage. Although this is a safety measure (called islanding protection) meant to safeguard technicians, it was a major downside that your system didn’t function just when you needed it most.
Hybrid inverters combine the pros of grid-tied and off-grid systems while eliminating their respective cons. They do this by supplying power through a battery in the event of a power cut. Owing to their flexible functionality, hybrid inverters have quickly become popular.
| Pros of Hybrid Inverters | Cons of Hybrid Inverters |
| Uninterrupted supply of power | Slightly more expensive |
| Less wastage of solar power | Difficult to modify existing systems |
Off-Grid Inverters
Off-grid inverters are those suitable for off-grid solar power systems. specifically, they are used in systems that rely on solar battery storage for backup power supply during nights or cloudy days. Off-grid inverters have integrated mechanisms for smooth charging of batteries — usually an MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracker) charge controller. This improves the battery’s charging efficiency while also protecting it and prolonging its life.
Off-grid inverters are designed for the simple job of charging/discharging batteries while powering your home. They can’t be integrated with the grid so can’t exchange power for net-metering or other purposes.
| Pros of Off-Grid Inverters | Cons of Off-Grid Inverters |
| Suitable for remote areas | No power exchange with grid |
How Much Do Solar Inverters Cost?
The price of solar inverters depends on many factors, including size, type and brand. Hybrid and off-grid inverters are slightly more expensive than grid-tied inverters, as discussed above. Larger-sized inverters are obviously more expensive than smaller ones, although the per-watt cost decreases with the inverter’s size.
As of 2022, a typical, single-phase 5 kW inverter’s cost varies between 1,000 and 2,000, based on brand and features. Microinverters can cost up to 20% more for the same system size, while hybrid inverters can often cross the 2,000 mark.
Inverter Market by Type (Solar Inverters, Vehicle Inverter, others), Output Power Rating (Upto 10 kW, 10-50 kW, 51-100 kW, above 100 kW), End User (PV Plants, Residential, Automotive), Connection, Voltage, Sales Channel Region. Global Forecast to 2027
The global inverter market size was valued at USD 16.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7% from 2022 to 2027. The growth of the inverter market can be attributed to growing investments in the renewable power generation technologies, green infrastructure. The rapidly usage of power backup systems in various sectors is also fueling demand for inverters.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Inverter Market Dynamics
Driver: Rising number of solar installations attributed to government-led incentives and schemes
Rapid developments in the solar energy sector in terms of power generation and utilization are contributing to the increase in the number of solar PV installations for various applications across the world. According to the Global Market Outlook for Solar Power/2022–2026—a report published by SolarPower Europe— global solar capacity doubled in 3 years from 2018, bringing the global solar fleet to one Terawatt capacity in April 2022. Solar is the fastest-growing renewable energy, representing over half of the 302 GW of renewable capacity installed internationally in 2021. Countries such as China, the US, Germany, and Japan are major markets with the highest number of new solar installations in 2019 and 2020. Flourishing solar energy markets, including India, Brazil, and China, are expected to create growth opportunities for the solar inverter system market. over, an increase in the number of global PV power plant installations is also creating potential growth opportunities for the solar inverter system market.
The governments of different countries undertake various schemes and initiatives to encourage the use of inverters in industrial applications. For instance, in 2020, China’s national energy administration (NEA) has set a target for renewable power to account for over half of total installed capacity by 2025 to help support the country’s emissions goals as a part of the 14th Five-year Plan (2021–2025). China was the largest PV market in the world in 2020. The Self-generation Incentive Program (SGIP – California only) and the US tax credits make solar and energy storage an attractive proposition for commercial end users. The demand for distributed PV in Europe has been driven by incentives provided by governments of different countries to promote residential and small commercial PV installations. The feed-in tariff (FiT) is a policy designed to encourage the adoption of all kinds of renewable sources of energy to reduce energy costs. The FiT policy typically includes three provisions: guaranteed grid access, a long-term fixed purchase price contract (generally of 20 years) for the electricity produced, and the decline in contract for new installations that are based on the cost of renewable energy generation with a downward trend toward grid parity. This policy was introduced in several major countries, including Germany, Italy, and the UK. Japan and China also have major PV FiT programs. These countries are expected to witness growth in the solar PV markets. With a guaranteed selling price of solar panels for 20 years, customers can make a reasonable return on their investments for a long time, thereby encouraging the installation of large systems on rooftops of buildings. These government incentives and schemes encourage solar companies to invest in solar projects. This, in turn, is acting as a growth driver for the market for inverters, especially solar inverters.
Restraint: Safety risks associated with high DC voltages
In traditional PV systems, PV panels, wires, and other equipment are energized with high DC voltages. These high DC voltages pose risks to installers, maintenance personnel, and firefighters. Solar inverters with PV arrays involve high DC voltages, making it difficult to isolate DC electric devices from PV arrays using DC isolation switches. When PV modules are connected in series, they create a high voltage, which can be dangerous for installers during the system installation. Under the condition of short-circuit current, there is a possibility of electric arcs, which can result in fire and a resulting threat to people in the vicinity of a PV system. These DC arcs are difficult to extinguish, posing a risk to firefighters. The fire can damage DC cables in PV arrays, thereby leading inverters to shut down automatically while manually isolating DC cables and other components. Safety mechanisms mandated by the National Electric Code (NEC) and the Electrical Safety Authority (ESA) of the US do not eliminate all risks, which hamper the growth of the inverter market.
Opportunities: Growing demand for electric vehicles
Inverters are used in automotive applications such as EV power trains. The DC power taken from vehicles’ batteries is converted to usable AC by these inverters. Vehicle inverters are used for operating onboard electronic systems and motors of vehicles. Continental (Germany), Delphi Technologies (UK), Toyota Industries (Japan), Sensata Technologies (US), Samlex Europe (Netherlands), and BESTEK (US) are some of the key manufacturers and providers of vehicle inverters.
Technological advancements in the automotive industry and the advent of trends such as connected, autonomous, and electric vehicles have increased the demand for electronic systems in vehicles. With the emphasis being laid on various environmental regulations, the electric vehicle market has witnessed decent growth globally. This, in turn, has led to the growth of its adjacent markets. The increasing propensity for electric vehicles among consumers is likely to drive the demand for vehicle inverters. Ambitious EV targets set by governments of different countries and required policy support have resulted in a decline in the costs of electric vehicles, extension in vehicle range, and improvements in charging infrastructures, which have further fueled the demand for electric vehicles globally. These factors are expected to create lucrative opportunities for the providers of vehicle inverters during the review period.
Challenges: Availability of low quality and cheap products in gray market and pricing pressure on manufacturers
The inverter market is highly fragmented, with many local and international players. Product quality is a primary parameter for differentiation in this market. The organized sector mainly targets industrial buyers and maintains higher product quality by following various industrial standards of the product. At the same time, the unorganized sector offers cheaper alternatives. The local manufacturers in most countries target the unorganized sector and compete strongly with global suppliers in the respective markets. The leading market players are currently facing stiff competition from the new players from the unorganized market, supplying cheap and low-quality products. These gray market players overpower the big players in terms of price competitiveness and local distribution network, which is a major challenge for the players operating in the inverter market.
Solar PV systems are witnessing increased global demand as they are used to generate green power to reduce dependence on grid power. With reduced of solar modules, inverters account for a large share of the overall installation costs of these modules. This results in downward price pressure on manufacturers of inverters. As the overall costs of residential, commercial, industrial, and utility-based solar systems are reducing, inverter companies are bound to reduce the of their products. Manufacturers of solar modules are enduring more pressure than the manufacturers of solar inverters in terms of reduction in the of their products. Manufacturers of solar inverters are finding it difficult to accommodate this change and allow price drops in their inverters. These price drops can be primarily attributed to the development of low-cost equipment and compressed profit margins, which are indicators of the overall price decline in inverters in the near future.
Market Interconnection
Automotive segment, by end user, is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during forecast period
The automotive segment is expected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The adoption of electric vehicles is growing substantially due to the implementation of emission regulations to limit the emissions from traditional vehicles. Apart from electric vehicles, the inverters are also used in conventional vehicles for on-board power appliances. These factors are thus responsible for the increased demand of vehicle inverters which is expected to fuel the growth for the automotive segment.
By output power rating, Below 10 kW segment is expected to be the most significant contributor to the global inverter market during the forecast period
By output power rating, the inverter market has been segmented into below 10 kW, 10 – 50 kW, 50 – 100 kW, Above 100 kW. Below 10 kW is expected to be the largest segment during the forecast period. These inverters with the power rating below 10 kW are commonly used in residential applications. The growth of the market can be mainly attributed to the increase the number of solar roof top installations in various countries. Mainly in Asia Pacific countries such as India and china, the government initiatives and schemes in developing solar pv systems is fuelling the growth of the below 10 kW segment.
“Asia Pacific: The largest and fastest inverter market”
Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the global inverter market between 2022–2027, followed by North America and the Europe. The inverter market in Asia Pacific is witnessing significant developments in the renewable energy sector due to increased initiatives towards climate change and net zero targets, which has supported the demand for inverters across countries of the region. The increasing investments in the photovoltaic (pv) plants, rise of installations in the residential sector along with the shift in transportation towards electrical vehicles in countries such as China, India, Australia, and Japan.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
The inverter market is dominated by a few major players that have a wide regional presence. The major players in the inverter market are Huawei Technologies (China), Sungrow Power Supply (China), SMA Solar Technology (Germany), Power Electronics (Spain), FIMER (Italy), SolarEdge Technologies (Israel), Fronius International (Austria), Altenergy Power System (US), Enphase Energy (US), Darfon Electronics Corporation (China), Schneider Electric (France). Between 2018 and 2022, the companies adopted growth strategies such as sales contracts to capture a larger share of the inverter market.
Scope of the Report
Report Attributes
from an estimated USD 16.3 billion in 2022 to USD 33.8 billion in 2027
Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities Challenges
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends
Inverter type, output power rating, output voltage, sales channel, connection type, end user, and region
Asia Pacific, North America, Europe, Middle East Africa, and South America
Updated financial information / product portfolio of players
Growing demand for electric vehicles
Rising number of solar installations attributed to government-led incentives and schemes
This research report categorizes the inverter market inverter type, output power rating, output voltage, sales channel, connection type, end user, and region
On the basis of sales channel:
On the basis of end user:
- Residential
- Automotive
- Photovoltaic (PV) Plants
- Others (Commercial, Industrial, and utilities)
On the basis of region:
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- North America
- Middle East Africa
- South America
- In March 2022, Huawei Technologies has signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Meienergy Technology Co., Ltd for providing Smart PV and energy storage system for the 1 GW utility PV plant and 500 MWh energy storage system in Ghana which is developed by Meienergy.
- In April 2022, Sungrow Power Supply has supplied string inverters to a 20.7 MW rooftop PV plant for electric vehicle manufacturing base of XPENG. The XPENG factory is now powered by 30% of clean electricity.
- In November 2019, SMA Solar Technology AG collaborated with South Korea-based LG Chem. Through this collaboration, the SUNNY BOY STORAGE battery inverters of SMA and RESU 10M batteries of LG Chem will be combined to form new home storage systems. The integration of SMA battery inverters with the RESU 10M batteries is expected to result in the development of integrated DC/DC converters, which can increase the operating voltage of batteries.
- In November 2021, FIMER made a contract with Indefol solar to supply inverter for Celadon sports Resort Club project. this project comprises 1,677 solar panels across a total surface area of 4,800 square meters. powered by 6 of FIMER’s PVS-100-TL three-phase string inverter solution
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the current size of the inverter market?
The current market size of global inverter market is USD 14.2 billion in 2021.
What is the major drivers?
The growth of the inverter market can be attributed to growing investments in the renewable power generation technologies, green infrastructure. The rapidly usage of power backup systems in various sectors is also fueling demand for inverters.
Which is the fastest-growing region during the forecasted period?
Asia Pacific is witnessing significant developments in the renewable energy sector due to increased initiatives towards climate change and net zero targets, which has supported the demand for inverters across countries of the region. The increasing investments in the photovoltaic (pv) plants, rise of installations in the residential sector along with the shift in transportation towards electrical vehicles
Which is the fastest-growing segment, by end user during the forecasted period?
The automotive segment is expected to be the fastest-growing segment in the inverter market. The adoption of electric vehicles is growing substantially due to the implementation of emission regulations to limit the emissions from traditional vehicles. Apart from electric vehicles, the inverters are also used in conventional vehicles for on-board power appliances. These factors are thus responsible for the increased demand of vehicle inverters which is expected to fuel the growth for the automotive segment
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION (Page No 29) 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES 1.2 DEFINITION 1.2.1 INVERTER MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.2.2 MARKET, BY END USER: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.2.3 MARKET, BY TYPE: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.2.4 MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.2.5 MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.2.6 MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 1.3 MARKET SCOPE 1.3.1 MARKET SEGMENTATION 1.3.2 REGIONAL SCOPE 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED 1.4 CURRENCY 1.5 LIMITATIONS 1.6 STAKEHOLDERS 1.7 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY (Page No 35) 2.1 RESEARCH DATA FIGURE 1 INVERTER MARKET: RESEARCH DESIGN 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA 2.1.1.1 Key data from secondary sources 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA 2.1.2.1 Key data from primary sources 2.1.2.2 Key data from primary insides 2.1.2.3 Breakdown of primaries 2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION 2.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH 2.2.1.1 Approach for arriving at market size using bottom-up approach (demand side) FIGURE 2 MARKET BOTTOM-UP APPROACH 2.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH 2.2.2.1 Approach for arriving at market size using top-down approach (Supply side) FIGURE 3 MARKET TOP-DOWN APPROACH FIGURE 4 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION METHODOLOGY: BASED ON SUPPLY SIDE ANALYSIS 2.3 MARKET BREAKDOWN AND DATA TRIANGULATION FIGURE 5 DATA TRIANGULATION 2.4 KEY ASSUMPTIONS FIGURE 6 ASSUMPTIONS FOR RESEARCH STUDY 2.5 FORECAST
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY (Page No 45) TABLE 1 INVERTER MARKET SNAPSHOT FIGURE 7 SOLAR INVERTER SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY TYPE, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 8 100–300 V SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 9 BELOW 10 KW SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY POWER RATING, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 10 GRID-TIED SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 11 INDIRECT SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 12 RESIDENTIAL SEGMENT TO LEAD MARKET, BY END USER, DURING FORECAST PERIOD FIGURE 13 ASIA PACIFIC TO DOMINATE MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS (Page No 50) 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES IN INVERTER MARKET FIGURE 14 GOVERNMENT-LED INITIATIVES RELATED TO PV PLANTS AND AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY TO DRIVE GROWTH OF MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD 4.2 MARKET, BY REGION FIGURE 15 ASIA PACIFIC MARKET TO REGISTER HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD 4.3 MARKET, BY TYPE FIGURE 16 SOLAR INVERTER SEGMENT DOMINATED MARKET IN 2021 4.4 MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE FIGURE 17 100–300 V SEGMENT DOMINATED MARKET IN 2021 4.5 MARKET, BY POWER RATING FIGURE 18 BELOW 10 KW SEGMENT HELD LARGEST SHARE OF MARKET IN 2021 4.6 MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE FIGURE 19 GRID-TIED SEGMENT HELD LARGER SHARE OF MARKET IN 2021 4.7 MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL FIGURE 20 INDIRECT SALES SEGMENT HELD LARGER SHARE OF MARKET IN 2021 4.8 MARKET, BY END USER FIGURE 21 RESIDENTIAL SEGMENT DOMINATED MARKET IN 2021
5 MARKET OVERVIEW (Page No 54) 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS FIGURE 22 INVERTER MARKET: DRIVERS, RESTRAINTS, OPPORTUNITIES, AND CHALLENGES 5.2.1 DRIVERS 5.2.1.1 Increasing investments in renewable energy sector FIGURE 23 GLOBAL NET SOLAR CAPACITY ADDITION (GW) FIGURE 24 GLOBAL INVESTMENTS IN RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN 2019 (USD BILLION) 5.2.1.2 Rising number of solar installations attributed to government-led incentives and schemes 5.2.1.3 Growing demand for residential solar rooftop installations and distributed energy resources (DERs) 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS 5.2.2.1 Safety risks associated with high DC voltages 5.2.2.2 Strain on batteries due to prolonged use of inverters 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES 5.2.3.1 Growing demand for electric vehicles 5.2.3.2 Increasing investments in development of Smart grids 5.2.3.3 Technological innovations in inverters and development of high-power density inverters 5.2.4 CHALLENGES 5.2.4.1 Availability of low-quality and cheap products in gray market and pricing pressure on manufactures 5.2.4.2 Shortage of components and parts due to COVID-19 crisis TABLE 2 REGION/COUNTRY-WISE PERCENTAGE DEVIATION FROM BENCHMARKS DUE TO COVID-19 5.3 PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS TABLE 3 INVERTER MARKET: PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS FIGURE 27 PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS 5.3.1 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES 5.3.2 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS 5.3.3 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS 5.3.4 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS 5.3.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY 5.4 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA 5.4.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS FIGURE 28 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS, BY END USER TABLE 4 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS, BY END USER (%) 5.4.2 BUYING CRITERIA FIGURE 29 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR END USERS TABLE 5 KEY BUYING CRITERIA, BY END USER 5.5 COVID-19 IMPACT ANALYSIS 5.5.1 COVID-19 HEALTH ASSESSMENT FIGURE 30 COVID-19 GLOBAL PROPAGATION FIGURE 31 COVID-19 PROPAGATION IN SELECTED COUNTRIES 5.5.2 COVID-19 ECONOMIC ASSESSMENT FIGURE 32 REVISED GDP FORECASTS FOR SELECTED G20 COUNTRIES IN 2020 5.6 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND FIGURE 33 AVERAGE SELLING OF INVERTERS OF DIFFERENT OUTPUT POWER RATINGS TABLE 6 AVERAGE SELLING OF INVERTERS OF DIFFERENT OUTPUT POWER RATINGS (USD) 5.7 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS FIGURE 34 INVERTER MARKET VALUE CHAIN 5.7.1 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT 5.7.2 COMPONENT PROVIDERS 5.7.3 MANUFACTURERS/ASSEMBLERS 5.7.4 SYSTEM INTEGRATORS AND DISTRIBUTORS 5.7.5 END USERS 5.7.6 POST-SALES SERVICES 5.8 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS’ BUSINESSES 5.8.1 REVENUE SHIFT AND NEW REVENUE S FOR INVERTER MANUFACTURERS FIGURE 35 REVENUE SHIFT FOR INVERTERS 5.9 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS 5.9.1 Z-SOURCE INVERTER 5.9.2 SOLAR MICRO-INVERTER 5.10 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS BETWEEN 2022 AND 2023 TABLE 7 MARKET: DETAILED LIST OF CONFERENCES EVENTS 5.11 MARKET MAP FIGURE 36 MARKET MAP FOR INVERTER 5.12 INNOVATIONS AND PATENT REGISTRATIONS TABLE 8 MARKET: PATENTS INNOVATIONS 5.13 TRADE DATA STATISTICS TABLE 9 ELECTRICAL STATIC CONVERTER MARKET: IMPORT STATISTICS, 2018–2021 (USD MILLION) TABLE 10 ELECTRICAL STATIC CONVERTER MARKET: EXPORT STATISTICS, 2018–2021 (USD MILLION) 5.14 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS 5.14.1 SUNGROW PROVIDES TURNKEY SOLUTION TO SOLAR POWER PLANT IN BARGAS, SPAIN, 2021 5.14.2 MAN TRUCKS BUSES, SOUTH AFRICA, DECIDED TO GO GREEN WITH GOODWE INVERTERS, 2021 5.14.3 FIMER PROVIDED INVERTER TO FIVE MID-LARGE SCALE SOLAR FARM PROJECTS IN REGIONAL SOUTH AUSTRALIA, 2021 5.15 TARIFFS, CODES, AND REGULATIONS 5.15.1 TARIFFS RELATED TO INVERTERS TABLE 11 IMPORT TARIFFS FOR HS 850440, ELECTRICAL STATIC CONVERTERS 5.15.2 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS TABLE 12 NORTH AMERICA: LIST OF REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS TABLE 13 EUROPE: LIST OF REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS TABLE 14 ASIA PACIFIC: LIST OF REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS TABLE 15 ROW: LIST OF REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS TABLE 16 GLOBAL: LIST OF REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS 5.15.3 CODES AND REGULATIONS RELATED TO INVERTERS TABLE 17 GLOBAL: CODES AND REGULATIONS
6 INVERTER MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING (Page No 82) 6.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 37 MARKET SHARE, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2021 TABLE 18 MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 6.2 BELOW 10 KW 6.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR RESIDENTIAL INVERTORS IN RESIDENTIAL SECTOR TO FUEL MARKET GROWTH TABLE 19 BELOW 10 KW: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 6.3 10–50 KW 6.3.1 EXPANDING COMMERCIAL SECTOR TO FUEL DEMAND FOR INVERTERS WITH 10–50 KW OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 20 10–50 KW: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 6.4 50–100 KW 6.4.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR SOLAR INVERTERS IN PV PLANTS AND VARIOUS INDUSTRIES TO BOOST MARKET GROWTH TABLE 21 50–100 KW: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 6.5 ABOVE 100 KW 6.5.1 RISING NUMBER OF PV PLANTS AND EXPANDING AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 22 ABOVE 100 KW: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
7 INVERTER MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE (Page No 87) 7.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 38 MARKET SHARE, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2021 TABLE 23 MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 7.2 100–300 V 7.2.1 RISING ELECTRICITY DEMAND TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 24 100–300 V: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 7.3 300–500 V 7.3.1 REQUIREMENT FOR UNINTERRUPTED POWER SUPPLY IN COMMERCIAL SECTOR AND VARIOUS INDUSTRIES TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 25 300–500 V: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 7.4 ABOVE 500 V 7.4.1 RISING INVESTMENTS IN DEVELOPMENT OF ON-GRID PV PLANTS TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 26 ABOVE 500 V: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
8 INVERTER MARKET, BY END USER (Page No 92) 8.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 39 MARKET SHARE, BY END USER, 2021 TABLE 27 MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 8.2 RESIDENTIAL 8.2.1 GOVERNMENT-LED INITIATIVES TO PROMOTE INSTALLATION OF ROOFTOP SOLAR SYSTEMS TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 28 RESIDENTIAL: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 8.3 AUTOMOTIVE 8.3.1 GROWING ADOPTION OF ELECTRIC VEHICLES AS NEW MODE OF TRANSPORTATION TO FUEL DEMAND FOR VEHICLE INVERTERS TABLE 29 AUTOMOTIVE: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 8.4 PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) PLANTS 8.4.1 INCREASING RENEWABLE ENERGY POLICIES IN SEVERAL COUNTRIES TO FUEL MARKET GROWTH TABLE 30 PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) PLANT: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 8.5 OTHERS TABLE 31 OTHERS: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
9 INVERTER MARKET, BY TYPE (Page No 97) 9.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 40 INVERTER MARKET SHARE, BY TYPE, 2021 TABLE 32 MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) TABLE 33 MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (THOUSAND UNITS) 9.2 SOLAR INVERTER TABLE 34 SOLAR INVERTER: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.2.1 CENTRAL INVERTER 9.2.1.1 Rising demand for central inverters in PV plants to drive market growth TABLE 35 CENTRAL INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.2.2 STRING INVERTER 9.2.2.1 Rising installation of solar panels in residential and commercial sectors to boost market growth TABLE 36 STRING INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.2.3 MICRO-INVERTER 9.2.3.1 Increasing demand for micro-inverters in residential sector to fuel market growth TABLE 37 MICRO-INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.2.4 HYBRID INVERTER 9.2.4.1 High-performance feature of hybrid inverters is driving market growth TABLE 38 HYBRID INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.3 VEHICLE INVERTER TABLE 39 VEHICLE INVERTER: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.3.1 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE (BEV) 9.3.1.1 Favorable government policies regarding EV vehicles globally to drive market growth TABLE 40 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.3.2 HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE (HEV) 9.3.2.1 Multi-functional program in hybrid electric vehicles to drive market growth TABLE 41 HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.3.3 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE (PHEV) 9.3.3.1 Increasing demand for EV vehicles to fuel market growth TABLE 42 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 9.4 OTHERS TABLE 43 OTHERS: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
10 INVERTER MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE (Page No 107) 10.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 41 MARKET SHARE, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2021 TABLE 44 MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 10.2 STANDALONE 10.2.1 INCREASING RURAL ELECTRIFICATION PROGRAMS IN SEVERAL REGIONS TO BOOST MARKET GROWTH TABLE 45 STANDALONE: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 10.3 GRID-TIED 10.3.1 GOVERNMENT-LED INITIATIVES TO INCREASE SOLAR ENERGY GENERATION TO DRIVE GROWTH OF GRID-TIED MARKET TABLE 46 MARKET, BY GRID-TIED, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 10.3.2 CONVENTIONAL INVERTER 10.3.2.1 Rise in installation of solar pv systems in residential and commercial sectors to drive market growth TABLE 47 CONVENTIONAL INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 10.3.3 Smart INVERTER 10.3.3.1 Technological advancements in grid-tied inverters to drive market growth TABLE 48 Smart INVERTER: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
11 INVERTER MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL (Page No 112) 11.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 42 INVERTER MARKET SHARE, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2021 TABLE 49 MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 11.2 DIRECT SALES CHANNEL 11.2.1 RISING PREFERENCE FOR DIRECTLY PROCURING VEHICLE INVERTERS AMONG AUTOMOBILE MANUFACTURERS TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 50 DIRECT SALES CHANNEL: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 11.3 INDIRECT SALES CHANNEL 11.3.1 INCREASING SALE OF INVERTERS IN RESIDENTIAL SECTOR AND PV PLANTS THROUGH INDIRECT CHANNELS TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH TABLE 51 INDIRECT SALES CHANNEL: MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
12 INVERTER MARKET, BY REGION (Page No 115) 12.1 INTRODUCTION FIGURE 43 INVERTER MARKET, BY REGION, 2021 (%) FIGURE 44 ASIA PACIFIC MARKET TO REGISTER HIGHEST CAGR FROM 2022 TO 2027 TABLE 52 MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) TABLE 53 MARKET, BY REGION, 2020–2027 (THOUSAND UNITS) 12.2 ASIA PACIFIC FIGURE 45 SNAPSHOT: MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC 12.2.1 BY OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 54 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.2 BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE TABLE 55 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.3 BY END USER TABLE 56 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.4 BY TYPE TABLE 57 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.5 BY CONNECTION TYPE TABLE 58 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.6 BY SALES CHANNEL TABLE 59 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7 BY COUNTRY TABLE 60 ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7.1 China 12.2.7.1.1 Rising electricity demand in various sectors and presence of favorable government policies to fuel demand for solar inverters TABLE 61 CHINA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7.2 India 12.2.7.2.1 Rise in number of solar rooftop installations and increasing Power Shortage to fuel demand for Inverters in India TABLE 62 INDIA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7.3 Australia 12.2.7.3.1 Presence of favorable government policies for solar energy generation to boost growth of solar inverter market in Australia TABLE 63 AUSTRALIA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7.4 Japan 12.2.7.4.1 Increasing investments in residential and PV utility-scale sectors to drive market growth TABLE 64 JAPAN: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.2.7.5 Rest of Asia Pacific TABLE 65 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3 NORTH AMERICA FIGURE 46 SNAPSHOT: MARKET IN NORTH AMERICA 12.3.1 BY OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 66 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.2 BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE TABLE 67 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.3 BY END USER TABLE 68 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.4 BY TYPE TABLE 69 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.5 BY CONNECTION TYPE TABLE 70 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.6 BY SALES CHANNEL TABLE 71 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.7 BY COUNTRY TABLE 72 NORTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.7.1 US 12.3.7.1.1 Increasing developments in solar energy field and favorable government policies to drive growth of solar inverter market in US TABLE 73 US: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.7.2 Canada 12.3.7.2.1 Rise in residential PV installations and supportive government policies to drive market growth TABLE 74 CANADA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.3.7.3 Mexico 12.3.7.3.1 Increased deployment of clean energy sources in Mexico to fuel market growth TABLE 75 MEXICO: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4 EUROPE 12.4.1 BY OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 76 EUROPE: MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.2 BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE TABLE 77 EUROPE: MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.3 BY END USER TABLE 78 EUROPE: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.4 BY TYPE TABLE 79 EUROPE: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.5 BY CONNECTION TYPE TABLE 80 EUROPE: MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.6 BY SALES CHANNEL TABLE 81 EUROPE: MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7 BY COUNTRY TABLE 82 EUROPE: MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.1 Germany 12.4.7.1.1 Growing automotive industry and rising adoption of renewable energy to drive market growth in Germany TABLE 83 GERMANY: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.2 UK 12.4.7.2.1 Increasing investments in battery production and solar power generation to drive market growth TABLE 84 UK: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.3 ITALY 12.4.7.3.1 Rising establishment of large-scale PV plants to fuel market growth TABLE 85 ITALY: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.4 France 12.4.7.4.1 Rising demand for solar inverters in PV plants to propel market growth TABLE 86 FRANCE: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.5 Spain 12.4.7.5.1 Expanding automotive industry to drive market growth TABLE 87 SPAIN: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.4.7.6 Rest of Europe TABLE 88 REST OF EUROPE: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA 12.5.1 BY OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 89 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.2 BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE TABLE 90 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.3 BY END USER TABLE 91 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.4 BY TYPE TABLE 92 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.5 BY CONNECTION TYPE TABLE 93 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.6 BY SALES CHANNEL TABLE 94 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.7 BY COUNTRY TABLE 95 MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.7.1 Saudi Arabia 12.5.7.1.1 Increasing power generation from solar resources to fuel demand for inverters TABLE 96 SAUDI ARABIA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.7.2 UAE 12.5.7.2.1 Rising efforts to develop electricity sector to create demand for inverters in UAE TABLE 97 UAE: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.7.3 South Africa 12.5.7.3.1 Expanding automotive industry and development of PV plants to fuel growth of inverter market in South Africa TABLE 98 SOUTH AFRICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.5.7.4 Rest of Middle East Africa TABLE 99 REST OF MIDDLE EAST AFRICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6 SOUTH AMERICA 12.6.1 BY OUTPUT POWER RATING TABLE 100 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT POWER RATING, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.2 BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE TABLE 101 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY OUTPUT VOLTAGE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.3 BY END USER TABLE 102 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.4 BY TYPE TABLE 103 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.5 BY CONNECTION TYPE TABLE 104 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY CONNECTION TYPE, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.6 BY SALES CHANNEL TABLE 105 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY SALES CHANNEL, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.7 BY COUNTRY TABLE 106 SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.7.1 Brazil 12.6.7.1.1 Increasing investments in solar energy technology to propel demand for inverters in Brazil TABLE 107 BRAZIL: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.7.2 Argentina 12.6.7.2.1 Government support to promote solar energy renewables to fuel market growth TABLE 108 ARGENTINA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION) 12.6.7.3 Rest of South America TABLE 109 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA: MARKET, BY END USER, 2020–2027 (USD MILLION)
13 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE (Page No 151) 13.1 KEY PLAYER’S STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN TABLE 110 OVERVIEW OF STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY TOP PLAYERS, JANUARY 2019 – MARCH 2022 13.2 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS OF TOP FIVE PLAYERS TABLE 111 MARKET: DEGREE OF COMPETITION FIGURE 47 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2021 13.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS OF TOP 5 MARKET PLAYERS FIGURE 48 TOP PLAYERS IN MARKET FROM 2017 TO 2021 13.4 COMPANY EVALUATION QUADRANT 13.4.1 STAR 13.4.2 PERVASIVE 13.4.3 EMERGING LEADER 13.4.4 PARTICIPANT FIGURE 49 MARKET (GLOBAL) COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX, 2021 13.5 STARTUP/SME EVALUATION QUADRANT, 2021 13.5.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANY 13.5.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANY 13.5.3 DYNAMIC COMPANY 13.5.4 STARTING BLOCK FIGURE 50 MARKET: STARTUP/SME EVALUATION QUADRANT, 2021 13.5.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING TABLE 112 MARKET: DETAILED LIST OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES TABLE 113 MARKET: COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES 13.6 INVERTER MARKET: COMPANY FOOTPRINT TABLE 114 TYPE: COMPANY FOOTPRINT TABLE 115 OUTPUT POWER RATING: COMPANY FOOTPRINT TABLE 116 BY END USER: COMPANY FOOTPRINT TABLE 117 REGION: COMPANY FOOTPRINT TABLE 118 COMPANY FOOTPRINT 13.7 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO TABLE 119 MARKET: NEW PRODUCT LAUNCHES, SEPTEMBER 2019–JANUARY 2022 TABLE 120 MARKET: DEALS, NOVEMBER 2019–MARCH 2022 TABLE 121 MARKET: OTHERS, NOVEMBER 2021–APRIL 2022
14 COMPANY PROFILES (Page No 169) 14.1 KEY PLAYERS (Business and financial overview, Products/solutions/services offered, Recent Developments, MNM view) 14.1.1 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES TABLE 122 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: BUSINESS OVERVIEW FIGURE 51 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 123 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 124 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 125 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: DEALS TABLE 126 Huawei TECHNOLOGIES: OTHERS 14.1.2 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD TABLE 127 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: BUSINESS OVERVIEW FIGURE 52 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 128 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 129 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 130 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: DEALS TABLE 131 SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO., LTD: OTHERS 14.1.3 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG TABLE 132 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: BUSINESS OVERVIEW FIGURE 53 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 133 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 134 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 135 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: DEALS TABLE 136 SMA SOLAR TECHNOLOGY AG: OTHERS 14.1.4 POWER ELECTRONICS TABLE 137 POWER ELECTRONICS: BUSINESS OVERVIEW TABLE 138 POWER ELECTRONICS: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 139 POWER ELECTRONICS: PRODUCT LAUNCHES 14.1.5 FIMER TABLE 140 FIMER: BUSINESS OVERVIEW TABLE 141 FIMER: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 142 FIMER: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 143 FIMER: DEALS TABLE 144 FIMER: OTHERS 14.1.6 SOLAREDGE TECHNOLOGIES TABLE 145 SOLAREDGE TECHNOLOGIES: COMPANY OVERVIEW FIGURE 54 SOLAREDGE TECHNOLOGIES: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 146 SOLAREDGE TECHNOLOGIES: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 147 SOLAREDGE TECHNOLOGIES: PRODUCT LAUNCHES 14.1.7 FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL TABLE 148 FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL: BUSINESS OVERVIEW TABLE 149 FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 150 FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 151 FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL: DEALS 14.1.8 ALTENERGY POWER SYSTEM TABLE 152 ALTENERGY POWER SYSTEM: COMPANY OVERVIEW TABLE 153 ALTENERGY POWER SYSTEM: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 154 ALTENERGY POWER SYSTEM: PRODUCT LAUNCHES 14.1.9 ENPHASE ENERGY TABLE 155 ENPHASE ENERGY: COMPANY OVERVIEW FIGURE 55 ENPHASE ENERGY: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 156 ENPHASE ENERGY: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 157 ENPHASE ENERGY: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 158 ENPHASE ENERGY: DEALS 14.1.10 DARFON ELECTRONICS CORPORATION TABLE 159 DARFON ELECTRONICS CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW FIGURE 56 DAFRON ELECTRONICS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2020 TABLE 160 DARFON ELECTRONICS CORPORATION: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 161 DARFON ELECTRONICS CORPORATION: PRODUCT LAUNCHES 14.1.11 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC TABLE 162 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC: BUSINESS OVERVIEW FIGURE 57 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 163 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 164 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC: DEALS TABLE 165 SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC: OTHERS 14.1.12 GENERAL ELECTRIC TABLE 166 GENERAL ELECTRIC: COMPANY OVERVIEW FIGURE 58 GENERAL ELECTRIC: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2021 TABLE 167 GENERAL ELECTRIC: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 168 GENERAL ELECTRIC: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 169 GENERAL ELECTRIC: OTHERS 14.1.13 DELTA ELECTRONICS TABLE 170 DELTA ELECTRONICS: COMPANY OVERVIEW FIGURE 59 DELTA ELECTRONICS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT, 2020 TABLE 171 DELTA ELECTRONICS: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED TABLE 172 DELTA ELECTRONICS: PRODUCT LAUNCHES TABLE 173 DELTA ELECTRONICS: DEALS TABLE 174 DELTA ELECTRONICS OTHERS Details on Business and financial overview, Products/solutions/services offered, Recent Developments, MNM view might not be captured in case of unlisted companies. 14.2 OTHER PLAYERS 14.2.1 CONTINENTAL 14.2.2 DELPHI TECHNOLOGIES 14.2.3 SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES 14.2.4 SAMLEX EUROPE 14.2.5 BESTEK 14.2.6 GOODWE 14.2.7 TMEIC 14.2.8 YASKAWA SOLECTRIA SOLAR 14.2.9 KACO NEW ENERGY 14.2.10 GROWATT NEW ENERGY 14.2.11 TBEA XINJIANG SUNOASIS
15 APPENDIX (Page No 216) 15.1 INSIGHTS OF INDUSTRY EXPERTS 15.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE 15.3 KNOWLEDGE STORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS’ SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL 15.4 AVAILABLE CUSTOMIZATIONS 15.5 RELATED REPORTS 15.6 AUTHOR DETAILS
The study involved major activities in estimating the current size of the global inverter market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the peer and parent markets. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Thereafter, market breakdown and data triangulation were used to estimate the market size of the segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
This research study on the inverter market involved the use of extensive secondary sources, directories, and databases, such as Hoovers, Bloomberg, Businessweek, Factiva, International Energy Agency, and BP Statistical Review of World Energy, to identify and collect information useful for a technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the global inverter market. The other secondary sources included annual reports, press releases investor presentations of companies, white papers, certified publications, articles by recognized authors, manufacturer associations, trade directories, and databases.
Primary Research
The inverter market `comprises several stakeholders such as inverter manufacturers, manufacturing technology providers, and technology support providers in the supply chain. The demand side of this market is characterized by the rising demand for inverters in residential, automotive, photovoltaic (PV) plants, commerical, industrial, and utility end users. The supply side is characterized by rising demand for contracts from the industrial sector, and mergers acquisitions among big players. Various primary sources from both the supply and demand sides of the market were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information. Following is the breakdown of primary respondents:
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the total size of the global inverter market. These methods were also used extensively to estimate the size of various subsegments in the market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following:
- The key players in the industry and market have been identified through extensive secondary research, and their market share in the respective regions have been determined through both primary and secondary research.
- The industry’s value chain and market size, in terms of value, have been determined through primary and secondary research processes.
- All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns have been determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources.
Global Inverter Market Size: Bottom-Up Approach
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size from the estimation process explained above, the total market has been split into several segments and subsegments. To complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for all the segments and subsegments, the data triangulation and market breakdown processes have been employed, wherever applicable. The data has been triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand- and supply sides. Along with this, the market has been validated using both the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Available Customizations:
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations as per the client’s specific needs. The following customization options are available for this report:
Top 8 Solar Inverter Suppliers in China
A solar inverter, also known as a PV inverter, is an electronic device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power homes, businesses, and the grid. The AC electricity produced by the solar inverter can be used immediately or fed into the electrical grid for later use.
The inverter plays a critical role in a solar energy system, as it ensures that the solar panels produce electricity at the right voltage and frequency to be usable. It also provides important safety features, such as protection against overloading and short-circuits, and monitoring of the solar panels’ performance.
Overall, a solar inverter helps optimize the performance of a solar energy system and makes the clean, renewable energy produced by the panels usable and accessible.
In this guide, I ranked and reviewed the top 8 solar inverter suppliers in China in 2023.
- Sungrow
- INVT
- Hoymiles
- SRNE
- Sorotec
- Atess Power
- Sineng
- Bluesun Solar
Cost Effective
Sourcing photovoltaic inverters from China can significantly reduce costs, as the cost of labor and materials in China is lower than in many other countries. This can result in lower costs for the manufacturer and ultimately lower for the end-user, which can make it an attractive option for those looking to invest in solar energy.
Abundant Supply
China is one of the largest manufacturers of solar inverters in the world, and has a large pool of manufacturers and suppliers. This means that there is a wide variety of solar inverters available from different manufacturers, which can provide a competitive advantage for those looking to source from China.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities
China has a long history of manufacturing and a strong technological base, and has invested heavily in the renewable energy sector in recent years. This means that many Chinese manufacturers have the latest technology and manufacturing capabilities, which can result in high-quality products and increased competitiveness in the market.
Types of Solar Inverters
There are mainly three types of solar inverters:
String Inverters
String inverters are the most commonly used type of inverters in residential and small commercial solar panel systems. They are called “string” inverters because they work by connecting a series or “string” of solar panels together and then converting the DC electricity generated by the panels into AC electricity.
In a solar panel system with a string inverter, all the panels are connected in a series, and the DC power generated by the panels is combined and then sent to the inverter. The inverter then converts the DC power into AC power that can be used to power homes and businesses.
String inverters are cost-effective and easy to install, making them a popular choice for small to medium-sized solar panel systems. However, if one panel in the series fails, the entire string will not produce power, so the system’s efficiency can be impacted. Additionally, the power output of the entire string is limited by the performance of the weakest panel in the series.
Microinverters
Microinverters are a type of inverter that are installed directly on each individual solar panel. Unlike string inverters, which convert the DC power generated by a series of panels into AC power, microinverters convert the DC power generated by each panel into AC power independently.
This means that if one panel in the system is not performing optimally, it will not affect the performance of the other panels. This makes microinverters a good choice for systems with panels that are exposed to shading, debris or other conditions that can reduce their performance.
Additionally, because each panel is independently optimized, the system’s overall power output is maximized, providing a higher efficiency compared to string inverters. Microinverters also have the advantage of providing real-time monitoring and optimization of each panel, which can help to improve the system’s overall performance.
However, microinverters are more expensive than string inverters and require more installation time and labor, as each microinverter must be installed directly onto each panel. This can make them a more expensive choice for small-scale solar panel systems.
Central Inverters
Central inverters, also known as large-scale or utility-scale inverters, are used in large commercial and industrial solar panel systems. They are called “central” inverters because they are located in a centralized location and convert the DC power generated by all the panels in the system into AC power.
In a solar panel system with a central inverter, all the panels are connected in a series and the DC power generated by the panels is combined and then sent to the inverter. The inverter then converts the DC power into AC power, which is then distributed to the electrical grid.
Central inverters are more efficient than string inverters for large-scale solar panel systems because they can handle a higher DC input power and generate a higher AC output power. Additionally, central inverters are more cost-effective than microinverters for large-scale systems because they do not require individual inverters to be installed on each panel.
However, central inverters have some drawbacks. If the inverter fails, the entire system will not produce power, and the cost of replacing a central inverter can be significantly higher than replacing a string inverter or microinverter.
Additionally, the performance of the entire system is limited by the performance of the central inverter, so if the inverter is not functioning properly, the system’s efficiency may be impacted.
Other types of inverters
Additionally, there are also hybrid inverters and battery inverters that combine the functions of an inverter and a battery system to provide backup power during power outages.
What are the Top Solar Inverter Suppliers in China in 2023?
My top picks are Sungrow, INVT, Hoymiles, SRNE, Sorotec, Atess Power, Sineng and Bluesun Solar.
Sungrow
Company Introduction
Founded in 1997 by Professor Cao Renxian, Sungrow is headquartered in Shanghai, China and has branches and offices around the world. The company offers a range of products including new energy power equipment, central inverters, string inverters, energy storage systems, and PV solutions.
Sungrow is a leader in the research and development of solar inverters, boasting the largest dedicated RD team in the sector and a wide range of products that include PV inverter solutions, energy storage systems, and NEV driving, EV charging, and renewable hydrogen production systems for utility-scale, commercial industrial, and residential applications.
than 150 countries are powered by Sungrow products.
Visit their website for more information.
INVT
Company Introduction
INVT is a company in the renewable energy industry, specifically in the field of solar energy.
INVT is a Chinese company that was founded in 2001 and is headquartered in Shenzhen, China. It is one of the top solar inverter manufacturers in China.
The company specializes in the development, production, and sales of solar inverters, energy storage systems, and related products. INVT is known for producing high-quality and reliable products and has a strong reputation in the industry.
The company has a growing global presence, with offices and branches in many countries around the world, and has established partnerships with companies in many countries around the world.
Visit their website for more information.
Hoymiles
Company Introduction
Hoymiles is a Chinese company that provides Smart energy management solutions, renewable energy solutions, including solar inverters, energy storage systems, and solar charge controllers.
Hoymiles was established in 2009 and is headquartered in Shenzhen, China.
The company offers a range of products that are designed to be reliable, efficient, and cost-effective. Hoymiles’ products are used in various applications, including residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar projects.
Hoymiles is one of the best solar inverter manufacturers in China that has a strong FOCUS on research and development, and invests heavily in the development of new products and technologies to stay at the forefront of the renewable energy industry.
Visit their website for more information.
SRNE
Company Introduction
SRNE is the abbreviation for Shenzhen Solar Energy Sources Co., Ltd., a Chinese company that specializes in the research, development, production, and sale of photovoltaic (PV) inverters and energy storage systems.
The company was established in 2010 and is headquartered in Shenzhen, China. SRNE’s product range include street light solar charge controllers, household solar charge controllers and off-grid all-in-one solar charge inverters.
Since its founding, SRNE has been awarded with more than 250 national technology patents and has been chosen as a Guangdong Province intellectual property demonstration organization.
Visit their website for more information.

Sorotec
Company Introduction
Sorotec is an established Chinese company that focuses on providing top-notch renewable energy solutions.
Founded in 2006 and based in Hangzhou, China, Sorotec specializes in the development, production, and sales of photovoltaic (PV) inverters and energy storage systems.
They offer a range of high-quality, efficient, and cost-effective products that are used in various applications, from residential to commercial and utility-scale solar projects.
As a result of years of accumulation and growth, Sorotec has established itself as a trustworthy supplier for China Mobile, China Unicom, China Tower, China Telecom, PetroChina, and State Grid. The company also ships to Europe, South America, the Middle East, Africa, Southeast Asia, and other regions.
The company’s major offerings include solar energy storage systems, active harmonic filters, static variable generators, low frequency UPS, high frequency UPS, outdoor UPS, and uninterruptible power supplies ranging from 1 KVA to 800 KVA (home use solar energy systems, Telecom base station solar power systems).
Visit their website for more information.
Atess Power
Company Introduction
Shenzhen ATESS Power Technology Co.,Ltd, a global provider of solar energy storage and EV charging solutions, was established in 2017 with the goal of creating and distributing accessible clean energy to every region of the globe.
ATESS has an advanced, automated manufacturing facility that is based in Shenzhen, China. To ensure quick shipment and after-sale support, an international service network with offices and warehouses has been established across 5 continents.
All-in-one hybrid inverters, battery inverters, and lithium battery solutions are just a few of ATESS’s product offerings.
Inverters are available from 5 kW to 1 MW, and they can be used for utility, commercial, and residential applications.
The EV charger portfolio consists of 7kW to 360kW AC and DC electric vehicle chargers for residential and public charging stations. These chargers are compatible with all widely available EVs, including e-buses and e-ferries.
Over 85 countries throughout the world have installed the company’s goods since it was created.
Visit their website for more information.
Sineng
Company Introduction
Sineng Electric Co., Ltd. is a Chinese high-tech company that specializes in the RD, production, trade, and maintenance of power electronic goods. These products include PV inverters, energy storage systems, power quality control, plant development, and other areas.
In the PV sector, Sineng offers all-scenario power generation solutions, ranging from 3kW to 6800kW central and string inverters. These inverters are widely used in ground mounted, floating, complex terrain, CI rooftop, and residential projects, and they can be customized to meet the needs of clients from all over the world.
Sineng offers all-scenario energy storage solutions, including 1000V/1500V central and string PCS and system integration products, which are applicable to the power generation side, the power grid side, the user side, and the micro-grid.
With regard to power quality management, Sineng offers a full selection of active power filters, Smart power quality correction devices, and other products that are used in a variety of sectors including communications, medicine, rail transit, petroleum and petrochemical, metallurgy, etc.
Visit their website for more information.
Bluesun
Company Introduction
Bluesun is a Chinese company that is highly focused on solar products and solutions.
Hoymiles was established in 1983 and is headquartered in Hefei, China.
The company offers a range of products that include solar panels, on-grid solar systems, off-grid solar systems, hybrid solar systems, batteries, inverters and even solar pumps.
Visit their website for more information.
Summary
Sourcing solar inverters from China has become a popular choice for many companies and individuals in the renewable energy industry. China is one of the largest manufacturers of solar inverters and has become a hub for the production of these products due to the availability of low-cost labor and materials.
Companies and individuals can benefit from the lower costs of production by sourcing their solar inverters from China, leading to increased profitability and competitiveness in the market.
However, sourcing solar inverters from China also has some challenges and risks. Quality control can be a concern, as some manufacturers in China may not adhere to the same quality standards as manufacturers in other countries.
Additionally, there can be issues with shipping and logistics, as the long distance between China and other countries can lead to delays and increased shipping costs.
To mitigate these risks, it is important to work with a reliable and trustworthy supplier when sourcing solar inverters from China. This includes conducting thorough research, visiting the supplier’s facility, and establishing clear and effective communication.
By taking these steps, companies and individuals can ensure that they are getting high-quality products at a competitive price, while also minimizing the risks associated with sourcing from China.